Spacecraft have visited the asteroids and increased our knowledge of these space critters that are so close to us, yet so far away.
Today's spacecraft exploring asteroids are the precursors to mining missions and have propelled us on our way to becoming capable of influencing the course of asteroids in the solar system!
Spacecraft Target Asteroids!
Many space probes have been sent to explore asteroids or as secondary targets for primary missions to comets. Comet missions are not discussed in the NEA pages. For information and links on comets please use Astra's Comets page.
Active Asteroid Missions and Flybys
Information on asteroid missions has been extracted from the websites that are linked in the short mission descriptions below. This section contains information on all asteroid missions, not necessarily Earth crossers. Please contact Astra with any omissions.
- Lucy Mission to Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids
- Osiris-Rex Target: (101955) Bennu, returned samples to Earth on September 24, 2023
- Hayabusa 2 # Target: 1998 KY26
Future Asteroid Missions
- NEO Surveyor (Near Earth Object Surveyor) - NASA infrared space telescope for hazardous near-Earth objects.
- Destiny Plus - JAXA's next asteroid mission
- Psyche Mission - Target: Psyche, main asteroid belt - Launched October 12, 2023.
- HERA - ESA Orbiter will study results from NASA's DART mission - Launched October 7, 2024.
- ZhengHe - Target : Kamo‘oalewa
- China mission to asteroid 2020 PN1 - Tentative 2026 launch
Completed Asteroid Missions
- NEOWISE - Mission ended July 31, 2024 due to lack of propellent.
- DART - Double Asteroid Redirection Test Mission Impact - Complete
- Dawn - Launched 2007, Asteroids: Ceres and Vesta
- Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer - WISE was Launched in 2009, the mission detected more than 33,000 asteroids
- Deep Impact - Launch: 2005, Encounter: 2002GT in 2020?
- Rosetta - Launch 2004, Asteroids: Steins and Lutetia
- Hayabusa Asteroid Sample Return Mission - Launch December 2014, Asteroid: Itokawa
- Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous Mission - NEAR Shoemaker, Launch 1996
- Stardust - Launched 1989, visited AnneFrank
- Galileo Mission - Launch 1989, Ida, Dactyl -
- Deep Space 1 - Launch: 1998, Asteroid: Braille
- Janus - SIMPLEx mission to 2 binary asteroids - CANCELED
Other Links for Asteroid Missions
Published papers on Asteroid Missions
Astra's Asteroid Retrieval Mission Page
Active Asteroid Missions
Lucy - visit 8 of Jupiter's Trojan asteroids
Launched: October 16, 2021

Lucy is NASA's first space mission to study the Trojan asteroids that orbit around the Sun in Jupiter's orbit, leading or following the planet. The mission name comes from the fossilized human ancestor that was named "Lucy" by her discoverers. NASA hopes the Lucy mission will revolutionize our knowledge of the formation of the solar system. After the spacecraft was deployed, it was determined that one of the solar arrays did not deploy completely. The partially deployed array is producing electricity and the mission continues. NASA was able to get the solar panel open to 353-degrees, a bit short of 360, but the mission should be successful.
Lucy measures more than 46 feet (14 meters) including solar panels. It has a 6.5-foot (2-meter) high gain antenna to communicate with Earth. Lucy will utilize boosts from Earth's gravity to complete a 12-year journey to eight different asteroids. After launch, Lucy will make 2 passes near Earth, using a "gravity assist" to speed up its journey to Jupiter's L4 trojan group, it will fly by trojan asteroids 3548 Eurybates and its satellite, Polymele, 11351 Leucus, and 21900 Orus from 2027-2028. It will then return to Earth to utilize another "gravity assist" and return to Jupiter's environment to the L5 trojans visiting a binary asteroid 617 Patroclus-Menoetius in 2033. In 2025 on the way to the L4, Lucy will fly by a Main Belt asteroid, 52246 Donaldjohanson, named for the discoverer of the Lucy fossil. After the L5 flyby, Lucy will continue cycling between the two Trojan clouds every six years.
The first instrument to be discussed is the Lucy Thermal Emission Spectrometer (L’TES) built by Arizona State University. It will measure the surface temperature of the Trojan asteroids. The Lucy LOng Range Reconnaissance Imager (L’LORRI) is a high resolution camera made by the Johns Hopkins University that will provide detailed images of the Trojan asteroids. L’Ralph is an instrument provided by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center it includes L’Ralph Linear Etalon Imaging Spectral Array (LEISA), an infrared imager to help identify different silicates, ices and organics that may be on the surface of the Trojan asteroids, and L’Ralph Multi-spectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC), that will take color images of the Trojan asteroids.
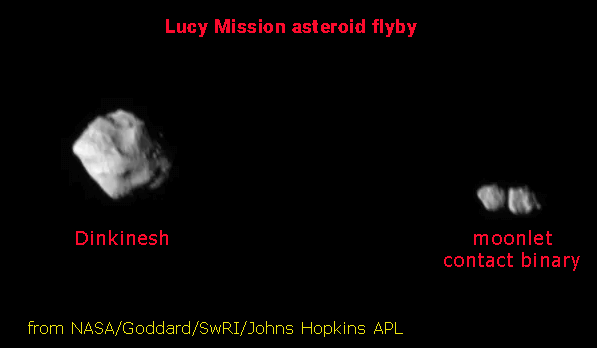
Lucy Flies by its First Asteroid: Dinkinesh
The Lucy spacecraft flew by a main asteroid belt, a small rocky asteroid named, Dinkinesh capturing images with the L’LORRI instrument. The image reveal that a small asteroid is in orbit with Dinkinesh. The asteroid's Ethiopian name means "you are wonderful". The Dinkinesh system is a close binary. The Lucy team estimates that the larger asteroid is ~0.5 miles or 790m at its widest. The smaller asteroid turned out to be a rarer kind of asteroid, a contact binary. The contact binary is thought to form when two asteroids that have gravitated toward each other until they touch so gently that they do not bounce away from each other. The moonlet is most likely material from Dinkinesh itself.
OSIRIS-REx / OSIRIS-APEX
Origins, Spectral-Interpretation, Resource-Identification, Security Regolith Explorer (OSIRIS-REx)
Launched: September 8, 2016 from Cape Canaveral.

The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft reached its target asteroid 101955 Bennu in September 2018. OSIRIS-REx landed on Benneu and returned a sample (60 grams or 2.1 ounces) to Earth. The sample will aid investigations of solar system planet formation and the origin of life. OSIRIS-REx reached Bennu on December 3, 2018 and performed its sample collection on October 20, 2020, successfully touching down on Bennu. OSIRIS-REx began its three-year cruise home carrying with it the first asteroid sample on May 10, 2021. Samples were returned to Earth and on September 24, 2023.

OSIRIS-REx has discovered that Bennu contains materials that originated from the asteroid Vesta. The material from Vesta is brighter than that on the dark asteroid Bennu. Spectral analysis shows that pyroxene is present in the material. As soon as the spacecraft arrived at Bennu, scientist Carl Hergenrother spotted particles flying off the asteroid. Bennu is releasing particles into space on a regular basis, particles 0.5 - 1 cm in size. Most of these fall back to the surface of the asteroid.
The Planetary Society ran a contest "Name that asteroid!" to find a name for the asteroid that mission planners choose for the OSIRIS-REx mission, 1999 RQ36. The asteroid was renamed Bennu by a 9-year old boy, Michael Puzio. Bennu was a large heron that was symbol of the Egyptian god, Osiris. More information can be found on the Planetary Society site and the OSIRIS-REx page.
OSIRIS-REx extended mission to Apophis
NASA has extended the OSIRIS-REx mission to orbit around near-Earth asteroid Apophis in 2029. NASA has given the mission a new name OSIRIS-APEX (OSIRIS-APophis EXplorer). Apophis, is roughly 1,200 feet (roughly 370 meters) in diameter--and will come within 20,000 miles or 32,000 km of Earth in 2029. OSIRIS-APEX will enter orbit around Apophis soon after the asteroid’s Earth flyby, for a close-up look scary S-type asteroid.
Find OSIRIS-REx mission news from University of Arizona at: OSIRIS-REx Status
Astra's asteroid catalog also features Apophis
HAYABUSA 2 - - now Hayabusa 2#
Hayabusa2's Sample-Return Capsule landed on Earth on December 6, 2020!

Hayabusa is the Japanese word for peregrine falcon. The Hayabusa2 spacecraft sent 5 target markers, 5 rovers, an impacter, and collected multiple samples from the asteroid 162173 Ryugu (type C) to be returned to Earth. Hayabusa 2 is the second asteroid mission, a follow-on to the Hayabusa mission that explored the asteroid Itokawa. Hayabusa 2 is possibly the most complex asteroid mission ever launched as of 2020. JAXA continues to build on the successful missions they have sent to deep space.
Hayabusa 2 arrived at Ryugu on June 27, 2018. In September 2018, the spacecraft deployed the MIcro-Nano Experimental Robot Vehicle for Asteroid (MINERVA-II1) to the asteroid’s surface. MINERVA-II1 carried Rover1A, (HIBOU) and Rover1B (OWL) that hopped across the surface of the asteroid gathering information on temperature, acceleration, and taking images of the surface. The rovers were identical and both had 2 cameras. In October 2018, Mobile Asteroid Surface Scout (MASCOT) was deployed. MASCOT was a joint French-German lander that also hopped to move. It made three hops, operating ~17 hours on Ryugu's surface, an hour longer than expected. The data on the asteroid’s composition it collected was sent back to Earth via the Hayabusa 2 spacecraft.
The spacecraft contained a device called Small Carry-on Impactor (SCI) that launched a 30-cm copper sphere impacting the surface and creating a crater 10m in diameter. It was launched toward Ryugu on April 4, 2019 and hit the surface traveling ~4,500 mph. Some of the debris was later collected by the orbiting Hayabusa spacecraft on July 11, 2019. To observe the impact, Hayabusa 2 carried a Deployable Camera (DCAM3) that separated from the main spacecraft to take the images. During the impact the spacecraft stayed safely on the opposite side of the asteroid while the camera watched the impact. What Hayabusa2 taught us about asteroids is that they are easily smashed to small pieces, making it hard if not impossible to protect Earth by smashing up an oncoming asteroid, instead its orbit must be changed before it reaches the home planet.
The Sample-Return Capsule (SRC) is brought its samples back to Earth. The spacecraft is landed in the Woomera Prohibited Area in Australia northwest of Adelaide on December 6, 2020. The spacecraft is guided by optical navigation. Because it is anticipated that the spacecraft will have half of the fuel (xenon) for the ion engine left, it will be sent on a second mission. That mission is now known as Hayabusa 2# and is heading for asteroid 1998KY26. It is expected to reach this target in July 2031. This asteroid is not a near-earth asteroid, but orbits between Earth and Mars.
+ + Learn more at JAXA about Hayabusa2
Future Asteroid Missions
NASA Future Asteroid Missions
16 Psyche - Main asteroid belt
Launch: October 13, 2023 - Arrival: August 2029

16 Psyche is a main belt asteroid orbiting between Mars and Jupiter. Psyche is large, about 226 km in diameter and is an M-type (metallic) asteroid. Because of its high iron and nickel content (it is similar to Earth’s core), it may be that Psyche is the exposed core of an ancient planet that lost its rocky outer layers due to violent collisions billions of years ago. Because of its high metal content, this asteroid could be a very valuable resource. Psyche orbits the sun every 1,830 days (5.01 years) and its distance from the Sun varies from 2.53 AU to 3.31 AU. Its orbit is between Mars and Jupiter and so never comes close to Earth and it is no threat to our planet.
The mission was be launched in October 2023. After launch, the spacecraft is traveling using solar-electric propulsion. With the help of a gravity assist from Mars, The Psyche spacecraft should arrive at the asteroid Psyche in August 2029. The Psyche mission will also test a new laser communication technology, called Deep Space Optical Communication, that encodes data in photons to communicate.
Psyche Science Instruments
Multispectral imager enables high-resolution imagery. It will use filters to identify the metals, silicates, or rocky materials of the asteroid Psyche. Powerful twin cameras can gather data on the geology, composition, and topography. One of the cameras also assists with optical navigation.
Gamma Ray and Neutron Spectrometer - will find the elements on the surface: iron, nickel, silicon, and oxygen. This equipment should reveal facts about the asteroid’s formation and its evolution.
Magnetometer - measuring Psyche's magnetic field should reveal much about its history and composition.
X-band Gravity Science Investigation - high-precision measurements of Psyche’s gravitational field combined with maps of the asteroid’s topography will reveal the asteroid's interior structure.
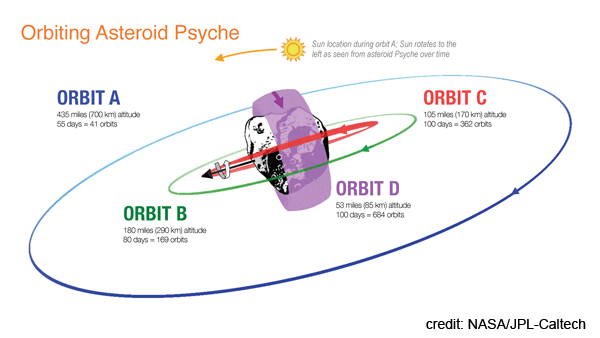
After arriving at Psyche in early 2026, the space craft will go into orbit around the asteroid. Initial orbit is at a high altitude – about 435 miles (700km) above the asteroid’s surface. Using electric propulsion it will move into lower orbits and conduct science investigations. It will drop to 180 miles (290km), 105 miles (170km), then into its final orbit (Orbit D) about 53 miles (85 km) above the surface.
Lindy Elkins-Tanton is the Principal Investigator of the Psyche mission. She is the Director of the School of Earth and Space Exploration at Arizona State University (ASU) in Tempe, AZ. You can read about Dr. Elkins in Astra's Featured Biographies of Extraordinary Women.

Psyche is unique in the solar system and the "heaviest" asteroid known. For more information check out the Psyche mission at the Arizona State University Psyche Mission website.
Find out more about 16 Psyche at Astra's Stargate
Janus
Unfortunately this mission has been canceled, completed spacecrafts have been mothballed.
Janus is a mission that will send two small spacecrafts named "Serenity" and "Mayhem" to two separate asteroids. Janus was scheduled to be a rideshare with Pscyhe mission on a Falcon Heavy rocket. The current targets are (35107) 1991 VH and (175706) 1996 FG3 although complications with the Psyche mission have caused the launch to slip. It is not currently known if these two targets can be attained or when Janus will launch.
NASA'sSmall, Innovative Missions for PLanetary Exploration (SIMPLEx) are intended to be low-cost planetary missions that development of science investigations that require a spaceflight mission that can be accomplished using small spacecraft.
NEO Surveyor (Near Earth Object Surveyor) - NASA
NASA’s NEO Surveyor is an infrared space telescope dedicated to hunting hazardous near-Earth objects. It is planned to launch in late 2027. It is a new step in NASA’s planetary defense strategy.
+ + Go to NASA's NEO Surveyor website
Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA)
Destiny Plus
DESTINY+ - Demonstration and Experiment of Space Technology for INterplanetary voYage with Phaethon fLyby and dUst Science
Destiny Plus will perform a close flyby of the asteroid Phaethon in January 2028 at a distance of only 500 kilometers. The spacecraft will run on ion engines (IES). It is the world’s first mission to escape from a near-geostationary transfer orbit into deep space using a low-thrust propulsion system. This spacecraft is based on Hayabusa2 technology.
DESTINY+ Science Instruments
DESTINY+ Dust Analyzer (DDA) developed under the leadership of the University of Stuttgart and the German Aerospace Center (DLR), will investigate the composition, mass, velocity, and direction of arrival of the dusts from Phaethon.
Telescopic CAmera for Phaethon (TCAP) - The instrument has an effective aperture of 120 mm, a focal length of 950 mm, and a field of view of 1.1 deg x 0.82 deg. A rotational mirror in the camera will be able to change the direction of the line of sight from 0 deg to 120 deg.
Multiband CAmera for Phaethon (MCAP) - The focal length is 55 mm, aperture ~21 mm, and the field of view is 18.9 deg x 14.2 deg. The MCAP can not rotate, it is fixed to the spacecraft. MCAP has multiple optics and sensors for each band and so has simultaneous multiband imaging.
Hayabusa 2
JAXA is now sending this successful spacecraft on a new mission after samples from the surface of an asteroid to the earth. The target 1998 KY26 has been chosen for the target, the resource below gives rationalization for the choice. Read JAXA's article about possible targets: Asteroid 2001 AV43 or 1998 KY26
Hayabusa 2 new mission is taking it to the small asteroid 1998 KYh26 and it should arrive in 2031.
This mission is a follow-up to the successful Hayabusa mission.
European Space Agency
Hera Asteroid Mission
As a followup to NASA’s DART mission, ESA's spacecraft Hera will make a detailed post-impact survey of the target asteroid, Dimorphos. Dimorphos is orbiting the binary asteroid known as Didymos. The Hera spacecraft will help to turn the impactor experiment into a repeatable planetary defence technique. In the world’s first test of asteroid deflection– HERA will demonstrate new technologies such as autonomous navigation around an asteroid and low gravity proximity operations. Hera will be humankind’s first probe to rendezvous with a binary asteroid system and Europe’s flagship Planetary Defender. HERA launched on October 7, 2024 at 10:52 am EDT from Cape Canaveral Space Station in Florida on a Falcon 9 rocket.

Hera will deploy a pair of CubeSats to aid in observations of the impact results: Milani will make spectral surface observations, and the CubeSat Juventas will make radar soundings within the asteroid. HERA and DART are part of the international cooperation Asteroid Impact Deflection Assessment (AIDA).
Hera Science Instruments
Two Asteroid Framing Cameras (AFCs) - These two identical cameras will assist navigation and scientific activities that require observations of the target asteroid from multiple positions and from various distances during the mission. They have a field of view that is 5.5 x 5.5 deg. These cameras will provide physical characteristics of the surface of the asteroids Didymos and Dimorphos as well as the crater created by DART and the Juventas landing zone.
Spectral Imager (Hyperscout-H) - Hyperscout-H is a hyperspectral imager working in a range between 665 and 975 nm (visible and near infrared). Developed by Cosine Remote Sensing, it makes observations in 25 distinct spectral bands. It is different from Cosine's standard Hyperscout.
Planetary Altimeter (PALT) - PALT is the Hera LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) instrument that emits a laser infrared light beam at 1.5 microns to determine distances. Its track on the ground is 1 meter at an altitude of 1 kilometer (1 milliradian). The altitude measurement accuracy is 0.5 meters. Its frequency is 10 Hertz. PALT will perform range measurements to determine asteroid 3D topography, fall velocity, asteroid wobble, and measure albedo. PALT can also be used to support navigation near the asteroids.
Thermal Infrared Imager (TIRI) - TIRI will use radio wave disturbances caused by the Doppler effect. This instrument will determine the mass of the two asteroids in the binary system, their gravity field, their rotational speed and their orbits. TIRI works using measurements during the radio exchanges between the Hera spacecraft and Earth as well as with the CubeSats.
Find out more at ESA about Hera
China National Space Administration (CNSA)
Tianwen-2 was (ZhengHe)
China is developing a combined asteroid sample-return and comet rendezvous mission known as Tianwen-2. The mission, expected to launch in 2025, will target Earth’s quasi-satellite 469219 Kamoʻoalewa aka 2016 HO3. This asteroid may possibly be a piece of material that blasted off the surface of the Moon. The craft will deliver samples to Earth and then undergo a seven year journey to rendezvous with main-belt comet 311P/PANSTARRS.
2020 PN1
CNSA announced that they plan to carry out an asteroid deflection test as part of a larger asteroid monitoring and defense system they are developing. The monitoring system will use ground-based and space-based instruments. It will be used to catalog near-Earth objects that may pose a threat. The mission will support CNSA's new planetary defense monitoring program. The agency will design and build a high thrust rocket that can carry a payload that will be designed to strike an asteroid with enough force to change its orbit. The target asteroid has not been announced but the mission may launch as early as 2025.
Available Papers on Asteroid Missions
Click on the link to navigate to the on-line papers that discuss Asteroid Missions:Mission opportunities with low delta V for NEA targets. This paper discusses 250 asteroids larger than 1 km considered easier to reach than the Moon's surface.
- Earth-Approaching Asteroids As Targets For Exploration - E. Helin and E. Shoemaker
Written in 1978, Gene Shoemaker and Eleanor Helin discuss the possibility of crewed missions to an NEA.
- Dynamical and Compositional Assessment of Near-Earth Object Mission Targets - Binzel and others
Written in 2002 for Meteoritics and Planetary Science. The authors identify 234 NEOs with having a calculated DV requirement of less than 7 km/sec as candidates for physical characterization and mission targets.
Completed Asteroid Missions
Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer
We thought it was all over!
NASA announced that it would Reactivate WISE for NEA searchers the week of 8/18/2013! The spacecraft was successfully revived in September 2013 after 31 months of hibernation. NASA's new mission home page can be found at WISE Mission Home.
Read about NEOWISE first discovery on December 29, 2013 - an NEA now designated 2013 YP139
WISE was a NASA-funded Explorer mission to study the solar system, the Milky Way, and the Universe in the infrared spectrum. WISE discovered over 153,000 asteroids. The WISE Mission launched on Dec. 14, 2009.
WISE found a new class of asteroid, the Earth Trojan.
WISE All-Sky Data Release provides access to WISE data. To look at data collected on asteroids, the WISE Moving Object Pipeline Subsystem (WMOPS) provides in depth information. Astronomers seeking data on individual asteroids, will want to check WISE Related Minor Planet Electronic Circulars (MPECs) for a list of the WISE discoveries.
The WISE mission website also offers educational videos at the NASA/JPL WISE Youtube channel!
NEOWISE was WISE
NASA's Near-Earth Object Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (NEOWISE) was reactivated by NASA from the Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) mission into a new mission detecting Near Earth Asteroids! The mission has been highly successful, discovering the potential hazardous asteroid 2013 YP139 in less than a week after it has been re-activated. The mission was given a 2-year extention in 2021. At that time, NEOWISE had made over 1.1 million infrared observations and studied 39,000 objects.
The NEOWISE/WISE mission ended on July 31, 2024. The spacecraft was shutdown due to lack of propellent. It will be replaced by NASA’s NEO Surveyor (Near Earth Object Surveyor), an infrared space telescope built for hunting hazardous near-Earth objects.
WISE details on Astra's Asteroid Missions Page
The Small Bodies Assessment Group - SBAG was established by NASA in March 2008 to establish scientific priorities and mission opportunities for exploration of near Earth asteroids and other small bodies. It provides input on the usability of asteroids and comets for human space exploration and other activities. SBAG reports its findings to NASA, but does not make recommendations.
DART - Double Asteroid Redirection Test Mission

Impact: September 26, 2022
The DART Asteroid mission is a planetary defense test of technologies to prevent an impact of Earth by a hazardous asteroid. It is an attemp to redirect an asteroid by forcing a collision with a spacecraft. Someday, a threatening asteroid may be redirected in this way. This is the first demonstration of the impactor technique to change the orbit of an asteroid in space.
DART was launched on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from the Vandenberg Space Base on November 24, 2021. It is traveling to a binary asteroid system called Didymos. Didymos is about half a mile in diameter (780m or 0.48mi), and like many asteroids it has a companion. The smaller asteroid, Dimorphos 525 feet (160m) in diameter is orbiting the larger asteroid every 11 hours and 55 minutes. The two are separated by 0.73 miles. After arriving at the system, DART spacecraft will impact Dimorphos nearly head-on. This should short the time it takes the small asteroid moonlet to orbit Didymos by several minutes.
The DART main instrument is the Didymos Reconnaissance and Asteroid Camera for Optical navigation (DRACO), a high-resolution imager. The camera is used to for navigation, to target the asteroid, to measure the size and shape of the asteroid, and to determine the impact site. DRACO is a narrow-angle telescope with a 208-millimeter aperture and field of view of 0.29 degrees. DART also carries a CubeSat made by Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI). It is called, Light Italian CubeSat for Imaging of Asteroids or LICIA.
LICIACube has two optical cameras to monitor the asteroids during flyby impact and aftermath. The narrow field or close-up camera is called, LEIA for LICIACube Explorer Imaging for Asteroid, and the wide field imager is called, LUKE for LICIACube Unit Key Explorer. Luke is equipped with an infrared filter. These cameras will capture the event and gather scientific data. The LUCIACube was successfully deployed from the DART spacecraft on September 18 and will be documenting the impact of the main craft.
DART at Didymos Mission Graphic
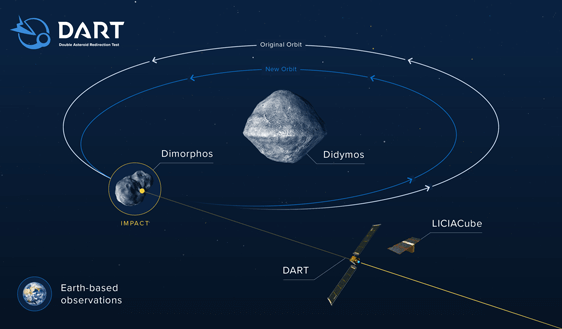
The moonlit Dimorphos passes in front of and behind Didymos as it orbits the larger asteroid as seen from Earth. This is called, an eclipsing binary system. Because of this Earth-based telescopes can measure the variation in brightness of the combined Didymos system to determine the orbit of Dimorphos. Because the asteroid is observable from Earth, Earth-based astronomers can make detailed observations before and after the impact. The asteroid is not close enough to Earth to become a hazardous object.
DART is a simple craft, not intended to make detailed observations. Its job is to impact Dimrophos in an attempt to change it's orbit. This planetary defense mission is being supported by the European Space Agency's (ESA) Hera probe. Find out more about HERA on this page.
See Astra's NEA Detection and Planetary Defense DART section.
Dawn Mission - Journey to the Beginning of the Solar System
Dawn revealed that Ceres is geologically active - - or was very recently.
The Dawn mission was part of NASA's Discovery Program operating until November 2018. Dawn orbited the main asteroid belt, Vesta, and is now journeying to Ceres. These are the two largest known asteroids and it is believed the they survived the early epoch of bombardment so evident on the surface of Earth's moon. The investigation showed that Ceres was active more recently than it was previous believed. At Vesta , Dawn showed that it was a more complex than expected.
The Dawn Mission launched on September 27, 2007. Dawn arrived at Vesta in June 2011 and reached Ceres in 2015 becoming the first to visit a dwarf planet and orbit two asteroids.
Asteroid Mappers - Citizen scientists help to map the surface of Vesta. Investigate and analyze high-resolution Dawn images of Vesta, including craters and other features, from your own computer!
Deep Impact - Comet Impact Mission
Launched on January 12, 2005, Deep Impact was highly successful at Comet Borrelly. Comets are composed of ice, gas and dust, and are believed to have formed in the solar system's most distant and coldest regions. They are thought to be time capsules that hold clues about the formation and evolution of the solar system. Deep Impact is a NASA Discovery Mission and is the first space mission to probe beneath the surface of a comet. The impactor weighed 370 kg or 816 lbs. The impact created a cloud of a fine, powdery material, not the water, ice, and dirt that was expected.
Deep Space has been given new tasks under the mission name of EPOXI. First it is to fly past comet Hartley 2 in in 2010. While travelling to Hartley 2, the spacecraft observed planets around other stars. Here is a link to a paper encouraging the Deep Impact new task, 2020-Jan-4 flyby of Potentially Hazardous Asteroid 163249 (2002 GT).
Rosetta
ESA reactivated Rosetta on 10 year journey to its target, Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko on January 20, 2014.
Sleeping Beauty awakes!
Rosetta was successfully launched on March 2,2004 from French Guiana. It made four gravity assists orbits, one by Mars and three by Earth, to reach it's target, Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. On its 10 year journey to the comet, the spacecraft flew by two asteroids: 2867 Steins on September 5, 2008) and 21 Lutetia on July 10, 2010).
Find out about Rosetta's NEA explorations during its journey to the comet by clicking on 2867 Steins and 21 Lutetia.
You can follow Rosetta on Facebook and Twitter. . .
Hayabusa and Hayabusa2
Launched on May 9, 2003, the Hayabusa spacecraft explored 25143 Itokawa (1998 SF36). This asteroid was named after the late Dr. Hideo Itokawa, considered the father of Japan's space development program. The HAYABUSA mission used an ion engine spacecraft to capture and return a sample from the asteroid. (1500 grains) It returned to Earth on June 13, 2010, dropping the sample in a capsule that landed in the Woomera Protected Area in Australia. This sample was found to contain a mere 1500 dust particles causing JAXA to build a second Hayabusa mission
HAYABUSA, was the first Japanese mission to an asteroid. The Hayabusa 2 mission is a follow-on mission to asteroid 162173 Ryugu. Haybusa 2 successfully returned its sample on December 5, 2020 and is off on a new mission to 1999 JU3. The new mission is designated, "Haybusa 2#" or "Haybusa 2 sharp."
Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous Mission
NEAR Spacecraft - The NEAR spacecraft visited the asteroids 253 Mathilde and 433 Eros (1898 DQ). The robotic space probe was designed by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory for NASA. In June 1997, the NEAR Shoemaker spacecraft flew within 1200 km of Mathilde, a 61 km diameter asteroid. It first flew by the Aten asteroid, Eros, (diameter 34 km) in December of 1998 and entered orbit on February 2000, becoming the first spacecraft to orbit an asteroid. It was renamed "NEAR Shoemaker", in honor of planetary scientist Eugene Shoemaker who dream of taking a geological sample from the surface of Eros. The successful mission closed with a soft landing on the asteroid February 12, 2001.
Full details can be found in the paper Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous: Mission Summary by Andrew F. Cheng the principal investigator. To investigate the orbit of Eros, go to the JPL's Small Body Database
Stardust - NASA Comet Sample Return Mission
Launched on February 7, 1989 with a primary mission objective to return a sample from the comet Wild 2, the Stardust visited the asteroid AnneFrank on November 2. 2002. The sample was returned to Earth in 2006.
Galileo - Jupiter Probe visits asteroids
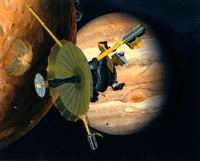 Launched on October 18, 1989, the Galileo spacecraft's primary mission was to explore the planet Jupiter as an orbiter and an impactor. On August 28, 1993 the spacecraft visited the asteroid 243 Ida, discovering that Ida had a small companion named Dactyl. Ida is 58 km long and 23 km wide. The successful mission was concluded in 2003 when the spacecraft made a controlled impact on the atmosphere of Jupiter. Images and artwork are courtesy NASA.
Launched on October 18, 1989, the Galileo spacecraft's primary mission was to explore the planet Jupiter as an orbiter and an impactor. On August 28, 1993 the spacecraft visited the asteroid 243 Ida, discovering that Ida had a small companion named Dactyl. Ida is 58 km long and 23 km wide. The successful mission was concluded in 2003 when the spacecraft made a controlled impact on the atmosphere of Jupiter. Images and artwork are courtesy NASA.

This image was used to help establish that 243 Ida had a moon.
Deep Space 1 - First Comet Flyby
Deep Space 1 launched on October 24, 1998. Its primary mission was to encounter Comet Borrelly and return science data and images from a comet. It performed a flyby of asteroid 9969 Braille (1992 KD) on July 28, 1999. The mission ended on December 18, 2001.


