
November 2022 - Vol. 26, No. 11
This Month's Night Sky - NOTE: The next paragraph describes the sky as it appears at 10 pm EST (11 pm EDT) near mid- month. The sky also looks this way at 11 pm EST (midnight EDT) during the beginning of the month and at 9 pm EST (10 pm EDT) by month's end.
If you are blessed with a dark observing site, the Orion arm of the Milky Way(the galaxy we inhabit) arches overhead from horizon to horizon. Embedded are the stars of constellations Cassiopeia, denoted by its familiar "W" or Sigma asterism, and Perseus. The Summer Triangle finally disappears early in the W. Although there are no bright stars due S., red Aldebaran and the tiny dipper asterism of the Pleiades, a famous open star cluster (Taurus), as well as yellow Capella (Auriga) glow in the SE. Later follows the twins, Castor and Pollux (Gemini), and the hour-glass asterism of constellation Orion with fuzzy M42 (Great Orion Nebula) just below its three "belt" stars, that heralds the coming of winter.
MERCURY too close to the sun to be observed is at superior conjunction on November 8. VENUS too close to the sun to be seen this month. MARS seems to move retrograde in Taurus shining at -1.7 mag by month's end. JUPITER still rules the night sky this month after last month's opposition. SATURN is in Capricornus, sets before midnight this month. URANUS is at opposition on the 9th. NEPTUNE is in Aquarius, setting well after midnight.
Review how to determine Angular Measurement.
Calendar of Events
NOTE: For those observers not in the ET zone, convert the calendar times to your zone's time by subtracting one hour for CT, two for MT and three for PT. Don't forget to adjust for Daylight Savings Time when necessary by subtracting one hour from your planisphere's time. Dawn and dusk times must also be corrected. See your local newspaper, TV news, or cable TV's Weather Channel for sunrise and sunset times or check with the U.S. Naval observatory. Unfortunately some of these events may occur during daylight hours in your area.
| DATE | EVENT |
| 01 | Saturn 4 deg. N. of Moon. |
| 04 | Jupiter 2 deg. N. of Moon. Neptune 3 deg. N. of Moon. |
| 05 | S. Taurid meteor peak, about 10 meteors per hour. |
| 06 | Daylight savings time (DST) ends for affected areas. |
| 08 |
Total lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon is closer to apogee. The entire eclipse will be visible from Africa and northeastern Europe. Parts of the eclipse will be visible from Asia, Australia, North America, and Antarctica. Mercury at superior conjunction. Uranus 0.8 deg. S. of Moon, occultation from most of Asia, most of Russia, Alaska, N. Greenland, Svalbard, and most of N. and W. Canada. |
| 09 |
Mercury at descending node. Uranus at opposition. |
| 11 | Mars 2 deg. S. of Moon. |
| 12 | N. Taurid meteor peak, about 15 meteors per hour. |
| 14 |
Moon at apogee. Alpha Geminorum, Pollux, 1.7 deg. N. of Moon. |
| 18 | Leonid meteor peak. Leonids meteor shower produces up to 20 meteors per hour. |
| 19 | Mercury at aphelion. |
| 21 | Venus at descending node. |
| 24 | Jupiter stationary, returns to prograde motion in the sky. |
| 26 | Moon at perigee. |
| 29 | Saturn 4 deg. N. of Moon. |
Lunar Almanac for November 2022
| Phases of the Moon | Phase and Date(s) | Best viewed before local midnight |
 |
New 23 |
Deep Space Objects |
 |
1st. Qtr 01 & 30 |
Planets & Moon |
 |
Full 08 |
Moon |
 |
Last Qtr 18 |
Deep Space & Planets |
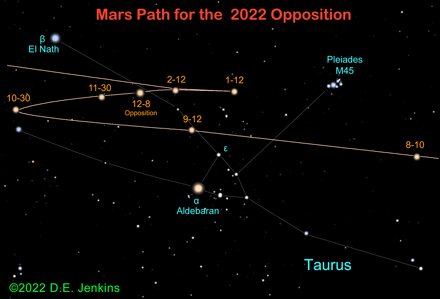
Topic of the month: Mars visits the constellation Taurus
Mars is in Taurus for the 2022-23 opposition that occurs on December 8, 2022. Mars appears to race through the sky as it approaches opposition, but must slow down and reverse its track as Earth begins to overtake it. The red planet will stay in Taurus for the rest of 2022.
Taurus is considered a fall constellation by observers in the northern hemisphere. Its alpha star, Aldebaran, and the open star cluster, the Pleiades (M-45) straddle the ecliptic. Aldebaran is a variable giant orange star that shines at .85 magnitude and so is considered a first magnitude star. It is called, the Eye of Taurus, Cor Tauri (heart of the bull), and Parilicium. Aldebaran's Arabic name means the follower, presumably because Aldebaran rose after the Pleiades. Aldebaran is located near an open star cluster, known as the Hyades. Before the distances of stars could be calculated, Aldebaran was considered part of the Hyades. There are about 100 stars in the Hyades that have been measured to be about 153 light-years away. These stars are about the same age, and have similar chemical characteristics, and are gravitationally bonded to each other so they travel through space together. It seems that the Hyades and Aldebaran shared the name Parilicium.
The Hyades cluster was featured in February 2016 What's Up almanac. Find that article by clicking this link.
The stars of Taurus are prominent and have a long history. The Pleiades alone could inspire a book or more with its colorful lore and the importance that have been attached to it by many cultures and the calendars it has helped to keep. The Pleiades is also an open cluster, with young bluish stars that are still surrounded by the wisps of the nebula they formed from. They are about 444 light years away, and thus are considered a "nearby" cluster. Mars doesn't venture close to the flashy cluster this opposition after a brief conjunction in early August.
The Pleiades cluster was featured in March 2020 What's Up almanac when Venus last visited them. Find that article by clicking this link.
On October 22, Mars passes 2.3 deg. N. of the star Zeta Tauri (mag. +2.9). This star is called, Tianguan and it marks the tip of the Bull's southern horn. Shortly after this, Mars' prograde motion will stop and it will stand at its first stationary point on October 30. Mars will continue to travel in Taurus until it reaches opposition. As the year of 2022 comes to an end, Mars will still be traveling backwards in Taurus.
Find out more at Astra's about. Mars Opposition December 8, 2022
Taurus, of course, is considered the constellation of the bull. This celestial image is interesting because only the front end of the bull is readily visible. The Hyades cluster makes up the bull's face. The horns of the bull end with Tianguan and El Nath. Oh, and El Nath is also part of the modern constellation of Auriga, where it stands in as the beta star of that constellation. Mars passed about 6 degrees below El Nath on October 9.
--See You Under the Stars!
Astra for Astra's Almanac
This installment of "What's Up?" is ©2022 by Dawn Jenkins for Astra's Stargate. View Ron Leeseburg's Farewell Issue for information on where to find information such as is presented in this almanac.