
October 2022 - Vol. 26, No. 10
This Month's Night Sky - NOTE: The next paragraph describes the sky as it appears at 10 pm EST (11 pm EDT) near mid- month. The sky also looks this way at 11 pm EST (midnight EDT) during the beginning of the month and at 9 pm EST (10 pm EDT) by month's end.
The Summer Triangle asterism, Vega (Lyra), Deneb (Cygnus) and Altair (Aquila), is still quite prominent overhead as darkness falls. Arcturus (Bootes) is now dipping to the NW horizon. From a dark site, the myriad stars of the Milky Way (the visible "arm" of our galaxy), "flow" eastwards through the "W" asterism of Cassiopeia and to bright Capella (Auriga) glowing in the NE. "The Great Square of Pegasus" asterism burns high in the SE while lonely Fomalhaut (Piscis Austrinus) shines far below, very close to the horizon. "The Big Dipper" asterism (Ursa Major) is nearly horizontal and now sits low on the N horizon. In the E, Aldebaran (Taurus) shines, a sure sign of Autumn.
MERCURY observable best in the northern hemisphere morning twilight, at least until mid-month. VENUS too close to the sun to be seen, reaches superior conjunction on October 22. MARS in Taurus will reach its first stationary point on October 30, and begin retrograde motion. Find out more in the monthly topic presented below. Mars will shine at -1.0 mag by month's end. JUPITER rules the night sky this month after its opposition on September 26th. This opposition Jupiter was closest to the Earth as it has been since 1963. SATURN, reaches its stationary point on October 23 and afterward returns to its prograde motion in Capricornus. URANUS is also moving retrograde and is occulted by the Moon in Aries on the 12th. NEPTUNE in Aquarius is still traveling retrograde.
Review how to determine Angular Measurement.
Calendar of Events
NOTE: For those observers not in the ET zone, convert the calendar times to your zone's time by subtracting one hour for CT, two for MT and three for PT. Don't forget to adjust for Daylight Savings Time when necessary by subtracting one hour from your planisphere's time. Dawn and dusk times must also be corrected. See your local newspaper, TV news, or cable TV's Weather Channel for sunrise and sunset times or check with the U.S. Naval observatory. Unfortunately some of these events may occur during daylight hours in your area.
| DATE | EVENT |
| 01 |
Mercury stationary. Mercury at ascending node. |
| 04 | Moon at perigee. |
| 05 | Saturn 4 deg. N. of Moon. |
| 06 | Mercury at perihelion. |
| 08 |
Mercury at greatest elongation W. (18 deg). Jupiter 2 deg. N. of Moon. Neptune 3 deg. N. of Moon. |
| 12 | Uranus 0.8 deg. S. of Moon, occultation from Mexico, W. United States, Alaska, Canada, northern Russia, Greenland, Iceland, and Scandinavia. |
| 15 | Mars 4 deg. S. of Moon. |
| 17 |
Moon at apogee. Alpha Geminorum, Pollux, 1.8 deg. N. of Moon. Mercury at greatest heliocentric lat. N. |
| 20 | Mars at ascending node. |
| 21 | Orionids meteor shower peak. This shower produces up to 20 meteors per hour. Meteors in this shower are generated by Halley's comet. The orbit of this periodic comet leaves a trail of dust particles on its way to the Sun. This trail of particles remains in this area of space until they encounter the Earth's orbit. This produces the annual shower. |
| 22 | Venus at superior conjunction. |
| 23 |
The Zodiacal Light or "false dawn" is visible in the E about 2 hours before sunrise. This pyramidal glow is caused by meteoroids, dust particles spawned by passing comets, etc., that have settled into the ecliptic plane (path followed by the Sun, Moon and planets), reflecting the Sun’s light before it rises here. This phenomenon will be visible for the next two weeks. Saturn stationary. |
| 25 | Partial solar eclipse observable from Europe, northern Africa, the Middle East, and western Asia. At greatest eclipse the Moon will cover 86% of the Solar disk. |
| 29 | Moon at perigee. |
| 30 | Mars stationary. |
Lunar Almanac for October 2022
| Phases of the Moon | Phase and Date(s) | Best viewed before local midnight |
 |
New 25 |
Deep Space Objects |
 |
1st. Qtr 02 |
Planets & Moon |
 |
Full 09 |
Moon |
 |
Last Qtr 17 |
Deep Space & Planets |
Topic of the month: Mars visits the constellation Taurus
Mars is in Taurus for the 2022-23 opposition that occurs on December 8, 2022. Mars appears to race through the sky as it approaches opposition, but must slow down and reverse its track as Earth begins to overtake it. The red planet will stay in Taurus for the rest of 2022.
Taurus is considered a fall constellation by observers in the northern hemisphere. Its alpha star, Aldebaran and the open star cluster, the Pleiades (M-45) straddle the ecliptic. Aldebaran is a variable giant orange star that shines at .85 magnitude and so is considered a first magnitude star. It is called, the Eye of Taurus, Cor Tauri (heart of the bull), and Parilicium. Aldebaran's Arabic name means the follower, presumably because Aldebaran rose after the Pleiades. Aldebaran is located near an open star cluster, known as the Hyades. Before the distances of stars could be calculated, Aldebaran was considered part of the Hyades. There are about 100 stars in the Hyades that have been measured to be about 153 light-years away. These stars are about the same age, and have similar chemical characteristics, and are gravitationally bonded to each other so they travel through space together. It seems that the Hyades and Aldebaran shared the name Parilicium.
The Hyades cluster was featured in February 2016 What's Up almanac. Find that article by clicking this link.
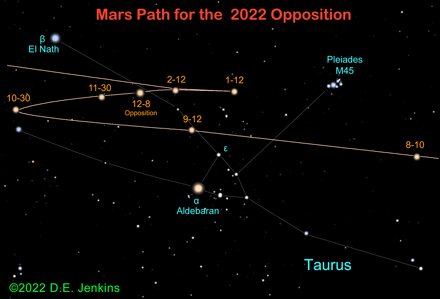
The stars of Taurus are prominent and have a long history. The Pleiades alone could inspire a book or more with its colorful lore and the importance that have been attached to it by many cultures and the calendars it has helped to keep. The Pleiades is also an open cluster, with young bluish stars that are still surrounded by the wisps of the nebula they formed from. They are about 444 light years away, and thus are considered a "nearby" cluster. Mars doesn't venture close to the flashy cluster this opposition after a brief conjunction in early August.
The Pleiades cluster was featured in March 2020 What's Up almanac when Venus last visited them. Find that article by clicking this link.
On October 22, Mars passes 2.3 deg. N. of the star Zeta Tauri (mag. +2.9). This star is called, Tianguan and it marks the tip of the Bull's southern horn. Shortly after this, Mars' prograde motion will stop and it will stand at its first stationary point on October 30. Mars will continue to travel in Taurus until it reaches opposition. As the year of 2022 comes to an end, Mars will still be traveling backwards in Taurus.
Find out more at Astra's about. Mars Opposition December 8, 2022
Taurus, of course, is considered the constellation of the bull. This celestial image is interesting because only the front end of the bull is readily visible. The Hyades cluster makes up the bull's face. The horns of the bull end with Tianguan and El Nath. Oh, and El Nath is also part of the modern constellation of Auriga, where it stands in as the beta star of that constellation. Mars passes about 6 degrees below El Nath on October 9.
--See You Under the Stars!
Astra for Astra's Almanac
This installment of "What's Up?" is ©2022 by Dawn Jenkins for Astra's Stargate. View Ron Leeseburg's Farewell Issue for information on where to find information such as is presented in this almanac.